A noise canceling earphone is a type of earphone that uses some method to reduce noise. At present, there are two types of noise canceling headphones: active noise canceling headphones and passive noise canceling headphones. The active noise reduction function is to generate a reverse sound wave equal to the external noise through the noise reduction system, and neutralize the noise, thereby achieving the effect of noise reduction. Passive noise canceling headphones mainly form an enclosed space by surrounding the ear, or use soundproof materials such as silicone earplugs to block external noise. Noise-cancelling headphones with active noise control are different from passive sound insulation for general headphones. The principle is: 1. First detect the low frequency noise (100 ~ 1000Hz) in the environment that the ear can hear by the signal microphone placed in the earphone. 2. Pass the noise signal to the control circuit, and the control circuit performs real-time operations. 3. Play back the sound waves with the opposite phase and the same amplitude as the noise through the Hi-Fi speaker to cancel the noise 4. After the superposition, the noise disappears and disappears. Active noise canceling headphones are expensive, but generally have excellent results and are comfortable to wear. However, independent battery power is required, and most passive noise canceling headphones can be used without power consumption (and no active noise reduction). Active noise reduction systems are divided into open loop systems, closed loop systems, and adaptive systems. Open loop system: The active noise reduction system collects noise through a microphone and produces an anti-noise signal. In an open loop system, as shown in the figure, the microphone is placed outside the earmuff, and the sound signal picked up by the inverting amplifier is outputted to obtain an anti-noise signal, and then mixed with the desired audio signal, and finally transposed in the earphone. Replay ridicule in the device. The anti-noise signal can attenuate external noise and make the original sound easier to understand. In general, open-loop active noise reduction systems can achieve noise attenuation of 10-15 dB, which is commonly found in different types of noise-cancelling headphones designed for professionals and consumers. However, this design is not suitable for those who want to adjust the size of the anti-noise signal to meet the best listening experience. The biggest advantage of an open loop system is simplicity, but it may not be the most satisfactory compared to other types of noise canceling headphones. Since the microphone is placed outside the earmuffs, the actual noise collected is not exactly the same as the noise heard in the earmuffs. In fact, the sound has changed through the earmuffs plus its internal reflections. Therefore, in many cases, anti-noise signals can be generated within the headphones. Closed loop system: If the microphone is placed in front of the transducer inside the ear cup, the system may generate a more accurate anti-noise signal as shown. At this time, the sound picked up by the microphone includes both the sound from the earphone transducer and the noise generated in the earmuff. This signal is fed back to the desired sound signal as an error correction signal, hence the name "closed loop system". . The operating characteristics of the closed circuit system are to achieve noise reduction through feedback. In cybernetics, noise (such as the distortion of an amplifier) ​​is seen as a nonlinear change that can be mitigated or eliminated by introducing a correction signal into the system. Shown is a closed loop active noise canceling headphone system. The microphone is placed inside the earmuff and the desired sound and noise mixture is picked up. First, the system separates the desired signal from the mixed signal and inverts the remaining noise signal. The inverted noise signal is then compensated to cancel out the noise in the closed loop system. The output stage re-synthesizes the anti-noise signal and the desired signal, ultimately enabling playback in the headphone transducer. Since this is a feedback process, in some cases, the closed loop system may be unstable. Adaptive system: Both the open-loop and closed-loop systems mentioned above use analog filters to generate anti-noise signals, while digital filters are more powerful and simpler to set up. The method of using digital filters to eliminate noise is called adaptive filtering, which can correct both phase errors and amplitude errors. The figure above is a schematic diagram of an adaptive active noise canceling headphone system. A microphone is placed on top of the headset to pick up the noise signal as a reference signal. The adaptive filter uses the transfer function of the current signal through the headphone system model to predict the noise inside the earmuff, and then inverts the predicted noise to the desired audio. The signals are superimposed and ultimately transmitted to the headphone transducer. The microphone placed in the earmuff picks up the actual sound and produces an error signal that causes the filter to converge to zero for a more accurate anti-noise signal. Active noise reduction technology has been developed for decades, and technology has matured. It is gradually extending from high-end applications to the civilian market, and the environment is also diverse. The most fundamental reason is that the active noise reduction processing mechanism enhances the space more than the passive noise reduction material science. However, the technical blockade is the most problematic problem in the industry. At present, several companies with active core noise reduction technology in the industry will not disclose their own technology. The technical blockade is obviously unfavorable to the development of the industry. However, this is not the development of noise reduction. At present, some domestic brands have independently developed active noise reduction technology, and this year will vigorously promote active noise reduction headphones. The environment we are facing is becoming more and more complex, and the environment in our life is getting bigger and bigger. It is the only purpose to bring noise-reducing headphones to the people and bring them to the mass consumer class. KNLE1-63 Residual Current Circuit Breaker With Over Load Protection
KNLE1-63 TWO FUNCTION : MCB AND RCCB FUNCTIONS
leakage breaker is suitable for the leakage protection of the line of AC 50/60Hz, rated voltage single phase 240V, rated current up to 63A. When there is human electricity shock or if the leakage current of the line exceeds the prescribed value, it will automatically cut off the power within 0.1s to protect human safety and prevent the accident due to the current leakage.
KNLE1-63 Residual Current Circuit Breaker,Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over Load Protection 1p,Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over Load Protection 2p Wenzhou Korlen Electric Appliances Co., Ltd. , https://www.zjaccontactor.com Active noise reduction headset principle

Active noise reduction system
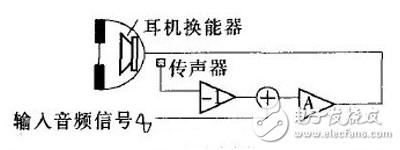
Open loop active noise canceling earphone system with external sensor 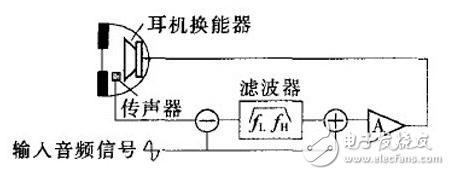
Closed-loop active noise canceling headphone system with built-in sensor 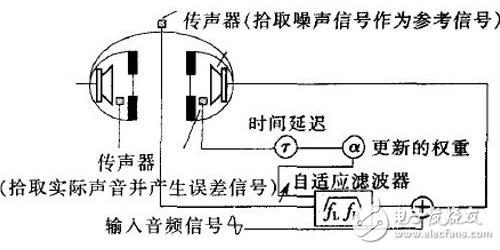
Adaptive active noise canceling headphone system to sum up
leakage breaker can protect against overload and short-circuit. It can be used to protect the line from being overloaded and short-circuited as wellas infrequent changeover of the line in normal situation. It complies with standard of IEC/EN61009-1 and GB16917.1.
Active noise canceling headphone principle and system
0 times
Window._bd_share_config = { "common": { "bdSnsKey": {}, "bdText": "", "bdMini": "2", "bdMiniList": false, "bdPic": "", "bdStyle": " 0", "bdSize": "24" }, "share": {}, "image": { "viewList": ["qzone", "tsina", "tqq", "renren", "weixin"], "viewText": "Share to:", "viewSize": "16" }, "selectShare": { "bdContainerClass": null, "bdSelectMiniList": ["qzone", "tsina", "tqq", "renren" , "weixin"] } }; with (document) 0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0] || body).appendChild(createElement('script')).src = 'http://bdimg.share. Baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion=' + ~(-new Date() / 36e5)];